|
Key Takeaway: Egress windows are required in all sleeping rooms for projects falling under the IRC and in many sleeping rooms for projects falling under the IBC. When required, the openings must meet specific egress window sizing requirements, and when provided below grade, must open into an area well.
If you are working on a residential design or construction project, an important design consideration is the requirement for egress windows. While most people in the design community understand what you are referring to with this term, “egress windows” is not actually defined in the code. The International Building Code (IBC) and International Residential Code (IRC) both refer instead to Emergency Escape and Rescue Openings (EEROs). In this article, we’ll refer to egress windows and EEROs interchangeably, but remember that the code only defines EEROs. A window can be used to meet the EERO requirements, but doors and other openings are also an option. All references are to the 2021 IBC and IRC. What is an Egress Window?
Egress Windows, or as the code calls them, EEROs, are defined in the IBC as “an operable exterior window, door or other similar device that provides for a means of escape and access for rescue in the event of an emergency.
Essentially, an egress window or EERO is a way for a building occupant to escape in the event of an emergency or for a first responder or other personnel to access a building for the purposes of rescue. A fire is the obvious emergency that comes to mind, but the openings could be used for any emergency situation. When are Egress Windows Required?
If you are working on a residential project in the United States, your building likely falls under one of two codes: the International Building Code or the International Residential Code. While the adoption of these codes varies by State and local jurisdiction, generally the IBC applies to apartments and larger residential facilities while the IRC applies to one and two family dwellings and townhouses. Many jurisdictions amend these codes, so be sure to check the applicable code enforced by your local authority having jurisdiction.
IBC Requirements
If your project falls under the IBC, emergency escape and rescue openings are required in the following occupancies (IBC 1031.2):
If you meet either of these conditions, then the IBC requires you to provide emergency escape and rescue openings in any basement or sleeping room below the fourth story above grade plane. There are numerous exceptions where EEROs would not be required:
IRC Requirements
If your project falls under the IRC, Emergency Escape and Rescue Openings are required in basements, habitable attics and every sleeping room. If the basement contains more than one sleeping room, an EERO is required in each sleeping room (IRC 310.1).
There are numerous exceptions where EEROs would not be required:
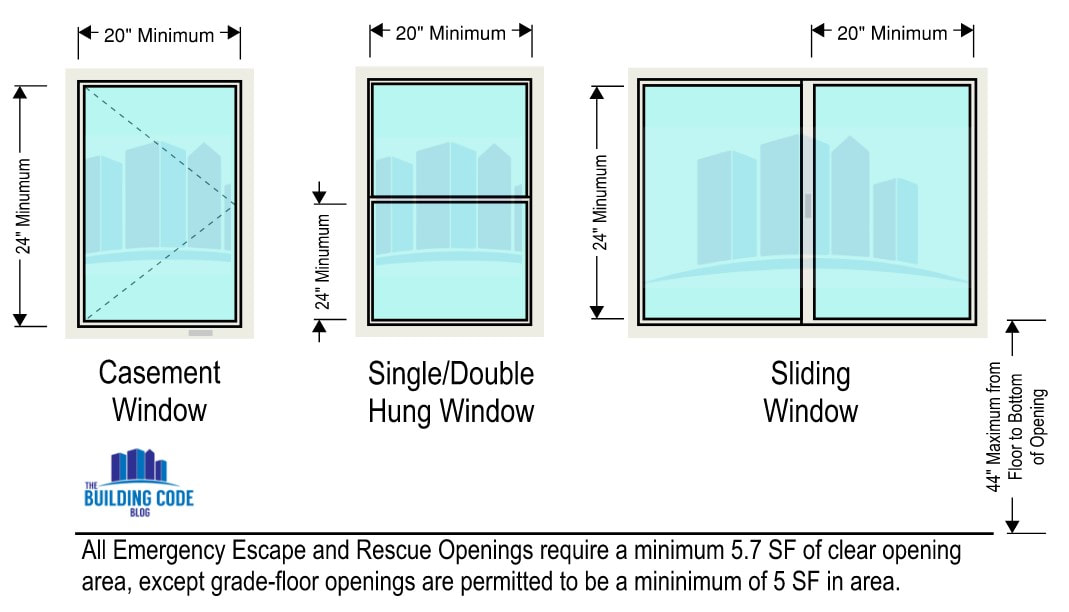
Egress Window Sizing Requirements
Both the IBC and IRC have the same dimensional sizing requirements for EEROs:
These dimensions are required to be a result of the normal operation of the window or door - you cannot break or alter the window/door in order to achieve the required dimensions.
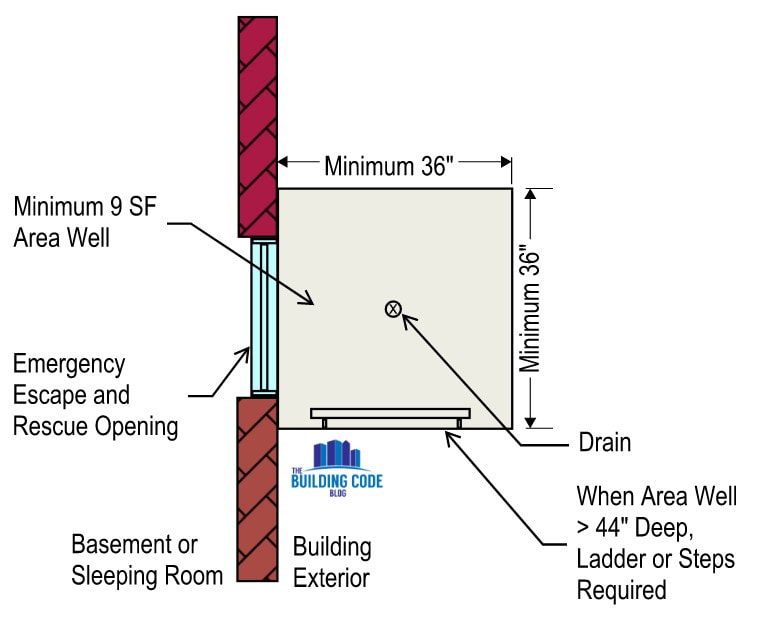
Basement Egress Windows
Area wells are required to be a minimum of 9 square feet in area with a minimum dimension of 36 inches in both length and width. The area well must also be of sufficient size to allow the EERO to fully open.
If the area well has a depth of more than 44”, a ladder or steps are required. The egress window or door opening into the area well cannot obstruct the ladder or steps when fully open.
If you choose to provide a ladder for the area well, the ladder must have an inside width of at least 12 inches, must project at least 3 inches from the area well wall and the ladder rungs must be spaced no more than 18 inches apart for the entire height of the area well.
If you choose to prove steps for the area well, the steps must have a minimum width of 12 inches, a minimum tread depth of 5 inches and a maximum riser height of 18 inches for the entire height of the area well. Finally, area wells are required to be connected to the buildings foundation drainage system unless the building is located on well-drained soil or sand-gravel mixture soils as defined by IBC 1803.5.1 and IRC 405.1 Bars, Grilles, Covers and Screens over Egress Windows
When bars, grilles, covers, screens or other similar devices are placed over EEROs or area wells, these devices cannot reduce the minimum required dimensions described above. Additionally, the bar, grilles, cover or screen must be releasable or removable from the inside without a key or tool and cannot require a greater force than what is required to open the EERO itself.
Summary
Egress windows, which the code refers to as “Emergency Escape and Rescue Openings” (EEROs) are required in all sleeping rooms for projects falling under the IRC and in many sleeping rooms for projects falling under the IBC.
When required, EEROs must meet the following size requirements:
If the EERO is below grade level, a minimum 36” x 36” area well is required. If the area well is more than 44” deep, a ladder or steps are required. Need assistance on your specific project? Add Campbell Code Consulting to your team. They are a full-service code consulting and fire protection engineering firm that can help you navigate complex code challenges.
4 Comments
Hi there, i’m not sure if this will be viewed or is monitored but my question is regarding the area of the window well so that the egress window can open fully. What if the egress window is a casement in swing window as opposed to an out swing window? Would it then be subject to the same 22 inch projection for escape as it is in the Ontario code? Many thanks, Steve.
Reply
2/16/2024 07:56:26 am
Window size is consistent regardless of the type of window. At Egress Pros we will install or sell in swing windows or sliders. Out swing windows create an obstacle in the well for a first responder and or inhabits. We would NEVER install a window with a crank out handle. Egress is about ease & speed. Even our screens are slider.
Reply
Marice Ballesteros
2/28/2024 02:46:34 am
Would like pricing for 2 windows with shipment to 64145. Concrete opening is 23 1/2 X 31 3/4. Thks.
Reply
Susan Wilson
7/19/2024 02:20:36 pm
I am trying to clarify IRC requirements. I have 1 sleeping room in the basement. It has a fixed window. You state IRC Requirements, "If the basement contains more than one sleeping room, an EERO is required in each sleeping room (IRC 310.1)."
Reply
Leave a Reply. |
Categories
All
Sign up to receive Building Code Blog UpdatesArchives
July 2024
|
The Building Code Blog
- Home
- Blog
- About
-
Tools
- Allowable Height & Area Calculator - Non-Separated Mixed Occupancy
- Allowable Height & Area Calculator - Separated Mixed Occupancy
- Average Grade Plane Calculator
- Calculated Fire Resistance for Wood Walls
- Fire and Smoke Damper Tool
- Fire Wall/Exterior Wall Intersection Tool
- Frontage Calculator
- IBC Occupant Load Calculator
- Plumbing Fixture Calculator
- Stair Pressurization Estimator
HomeAboutBlogContact |
Copyright © 2019-2024 The Building Code Blog
The views, opinions, and information found on this site represent solely the author and do not represent the opinions of any other party, including the author's employer and the International Code Council, nor does the presented material assume responsibility for its use. Local codes and amendments may vary from the code requirements described herein. Fire protection and life safety systems constitute a critical component of public health, safety and welfare and you should consult with a licensed professional for proper design and code compliance.
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
